[ad_1]
The Soviet-designed T-72 main battle tank (MBT) wasn’t the most produced armored vehicle of the 20th century; that honor goes to the T-54/55. However, the Cold War-era T-72 has a more ominous distinction — namely that it’s now likely the most destroyed tank in history.

According to data from the Ukrainian military, open-source military hardware tracker Onyx and Pentagon estimates, some 2,000 Russian T-72s have been destroyed in the fighting in Ukraine. Dozens, if not hundreds more have been captured as Russian tank crews have abandoned their tanks. In addition to the Ukraine War tally, a large number of this breed of tank had also been destroyed during the 1991 Gulf War.
The Secret T-72
Losses like these certainly weren’t expected when the T-72 was introduced in 1973. The tank was actually quite feared by Western observers, who spent more than a decade trying to even get a close-up view of one. There are even stories that when mock-ups of the T-72 were produced for the 1984 film Red Dawn — using the chassis of a surplus M8A1, which was based on the M41 Walker Bulldog — the CIA even took an interest.
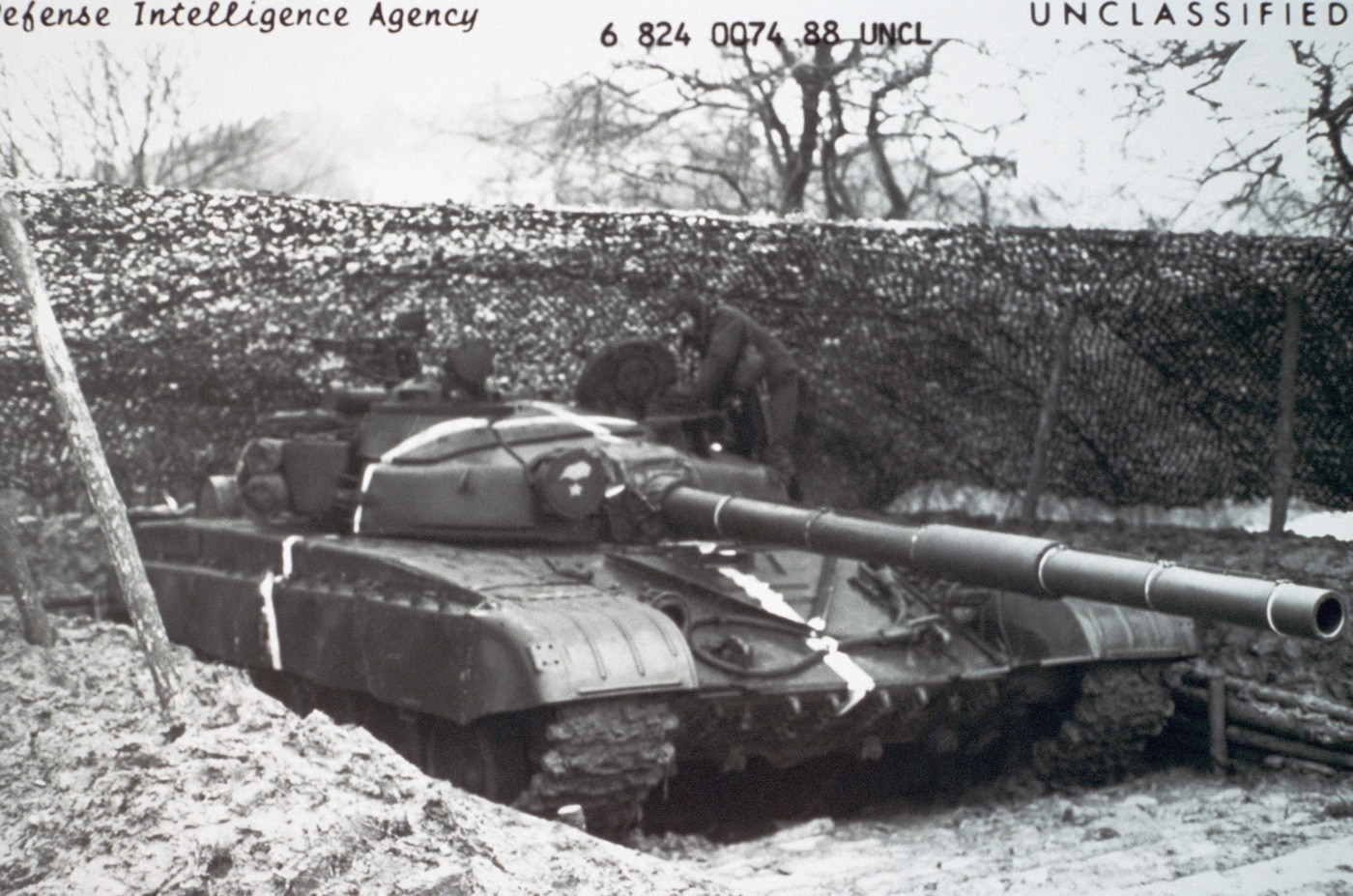

A New York business had attempted that same year to smuggle two T-72 tanks out of Poland without luck. Just a few years later, Oliver L. North even attempted to trade weapons to Iran for a captured Soviet-made T-72 during the Iran-Iraq War. That effort didn’t get very far, however.
Another time, U.S. officials managed to convince a Romanian connection to sell a T-72. The tank was even loaded on a boat, but then reports surfaced that Soviet submarines were on patrol in the Black Sea and the deal was sunk over fears that the ship carrying the MBT might meet such a fate!
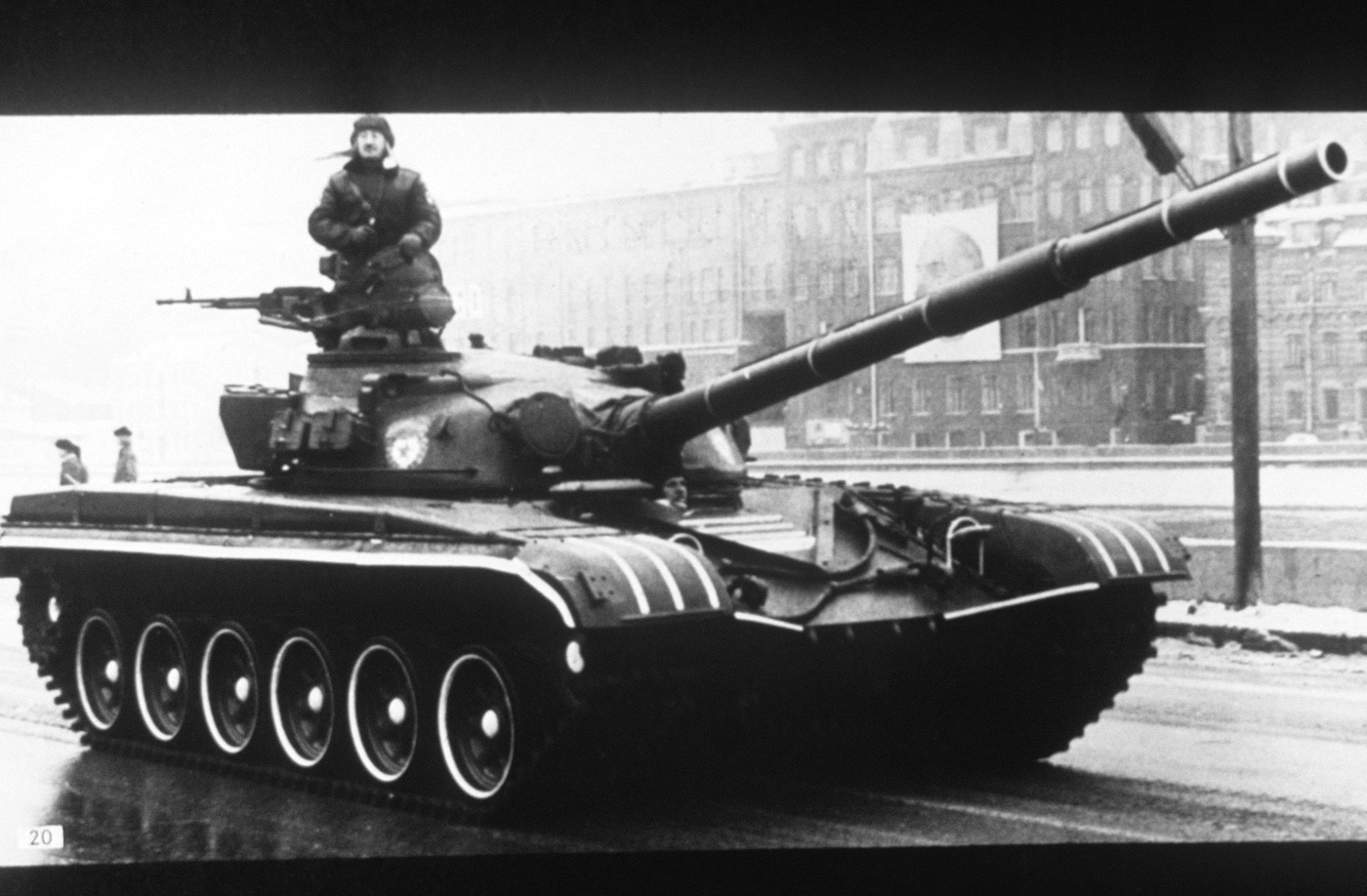

Finally, a Romanian arms dealer sold a T-72 to American agents in 1987 under the guise of scrap metal. By that time the tank had been in service for 14 years, and its design was already superseded by more advanced tanks.
A Notable Step Forward
There were plenty of reasons why the U.S. wanted to see the T-72 up close. When it was introduced in the mid-1970s, it was noteworthy at the time for having a crew of three compared to the four of Western MBTs. In addition, it used an autoloader to increase the rate of fire for its 2A46 125mm main gun. The theoretical rate of fire was eight rounds per minute, but it has been shown in practice that this was especially optimistic. That autoloader also presented some serious problems, something we’ll get to in a minute.
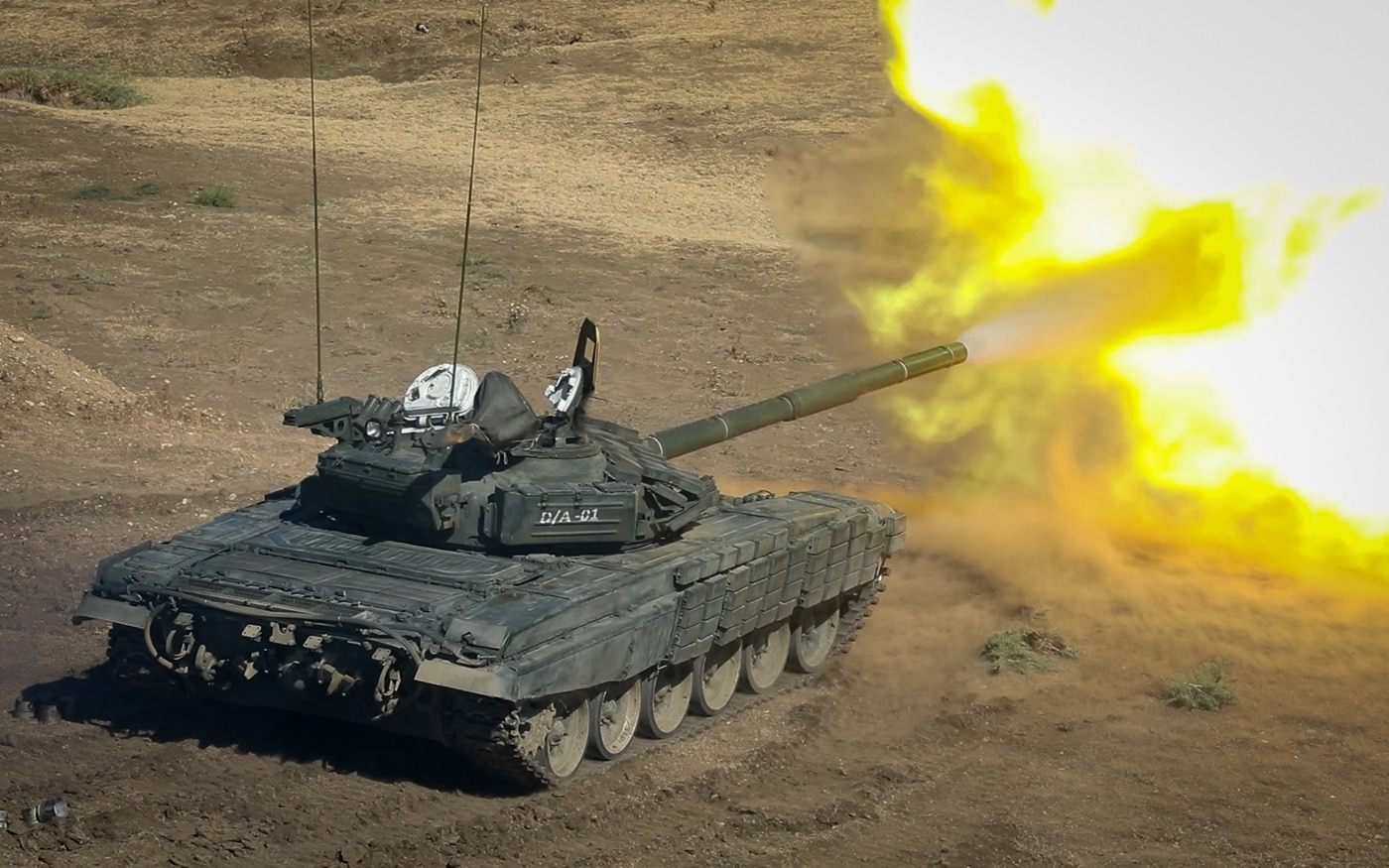

All T-72s built for use by the armies of the former Warsaw Pact also had an interior lining that featured a special synthetic, lead-based material, which was intended to provide some degree of protection against two of the products of a nuclear explosion — namely to help the crew against neutron radiation, and for the electronic equipment against electromagnetic pulses.
The MBT was also developed to cross rivers — and in theory, the system is sound. In practice, however, it could be described as “terrifying,” as it involved a narrow snorkel tube for deep-fording rivers. This snorkel fits over the gunner’s periscope mounting, and could allow the hull to travel “underwater” but without any easy method for the crew to escape should the tank become bogged down in the silt. Unsurprisingly, the whole tactic of fording rivers was quite unpopular with Russian soldiers.
Steadily Upgraded
The T-72 MBT was steadily upgraded, a point that continued even after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. This included a variety of improvements including a new type of diesel engine, enhanced suspension and armor protection, as well as additional defensive features including a smoke-grenade launcher.

After the end of the Cold War, upgrade packages were offered by Russia, but also by Ukraine, France, and Serbian-based companies.
The T-72 tank has been used in significant numbers in Ukraine, even as the Kremlin has developed more advanced MBTs, notably the T-90.

“The Russians don’t have significant numbers of new tanks, and instead they have utilized large numbers of their older tanks that have been equipped with some new technology,” explained Robert A. Sanders, distinguished lecturer of national security at the Henry C. Lee College of Criminal Justice and Forensic Sciences at the University of New Haven.

“What is surprising is that there is evidence of in-country manufacturing — someone is shipping parts to Russia in violation of the sanctions,” said Sanders. “But we’ve seen that Russia is increasingly unable to replace what it is losing on the battlefield.”
A Serious Design Flaw
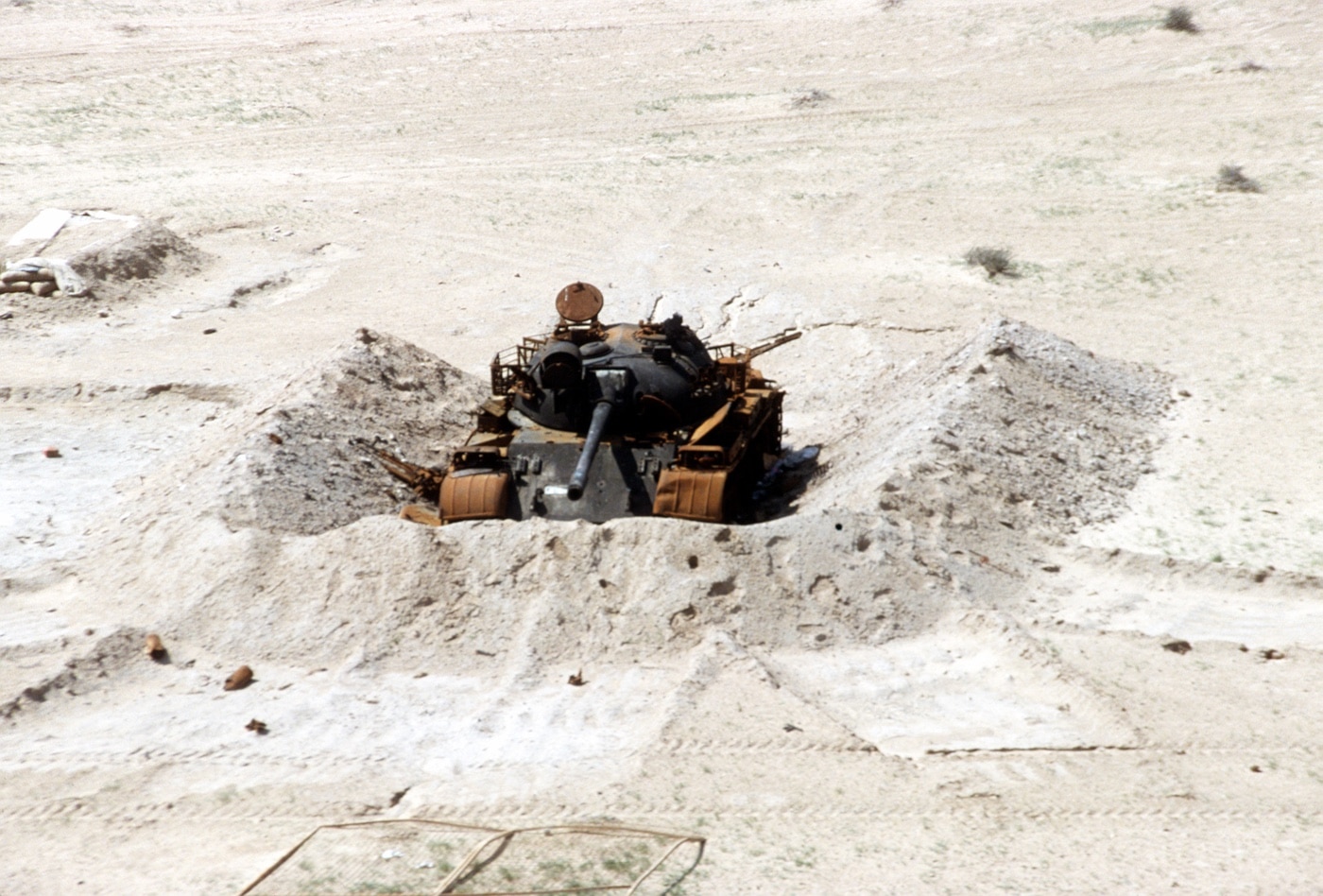
The T-72 first saw service in the Iran-Iraq War of the 1980s, but it was during the 1991 Gulf War that a notable flaw was discovered. The ammunition for the main gun sits in a carousel-style automatic loader with multiple shells within the turret. Even an indirect hit can start a chain reaction that often sets off the entire store of up to 40 rounds.
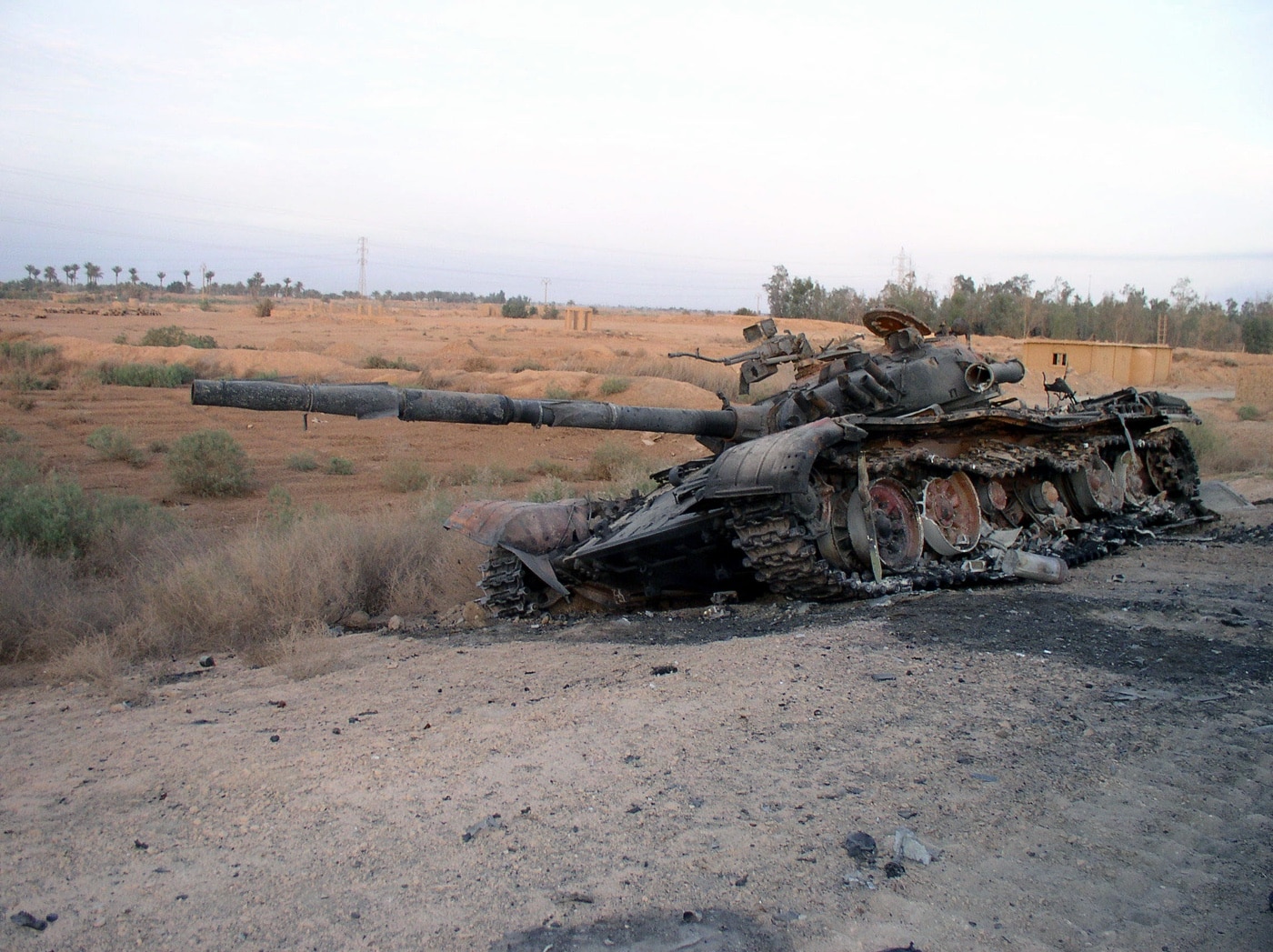

The resulting shockwave from even a dozen rounds is enough to blast the tank’s turret as high as a two-story building — which has come to be known as the “jack-in-the-box” effect. The flaw was first detected during the U.S.-led invasion of Kuwait to liberate the country from Iraq in 1991. However, the Russian military never bothered to resolve or even address the issue.

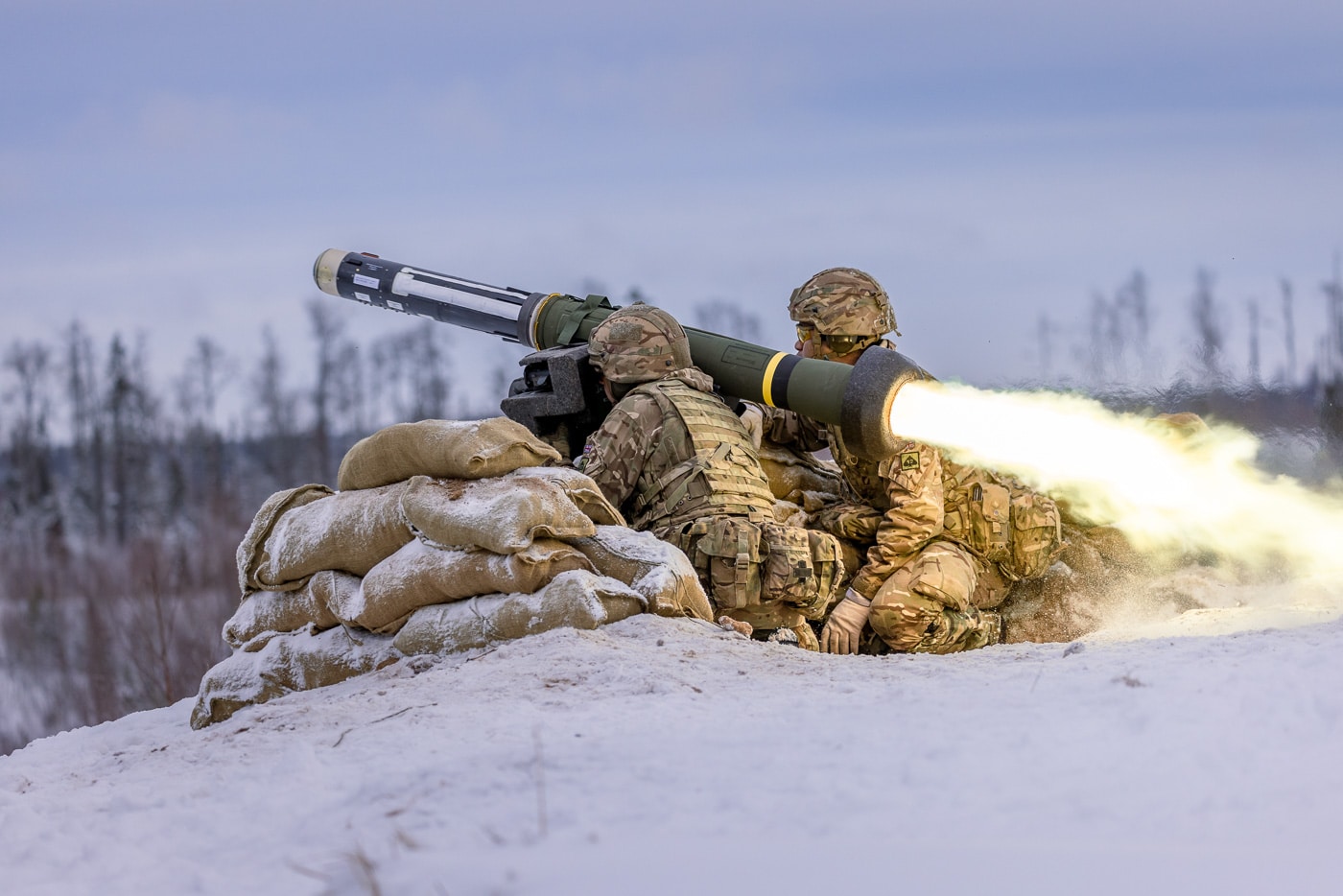
It is apparently made all the worse as modern man-portable anti-tank weapons such as the American-made FGM-148 Javelin can target the T-72 with an arc of fire that strikes at the junction of the hull and turret.

“After the end of the Cold War, the Kremlin likely never thought they’d face a Western enemy — or at least a Western-supported enemy — that could exploit the particular design flaw,” suggested Sanders. “Likewise, Russia failed to adequately improve these tanks as the Russian Army was looking forward, even as they had vast amounts of tanks in storage. Russia’s oil-based economy doesn’t really work all that well, and there isn’t often the additional money to fix the old stuff while building the next generation. This is true of not only the tanks but of their aircraft and even infantry equipment.”

Thus, the problem of the autoloader hasn’t been addressed, even with the most “modernized” models. In fact, the T-90 series — the successor to the T-72 and developed from it — that entered service in 1992 features upgraded armor, but its ammunition loading system remains similar to its predecessors. It is seen as just as vulnerable due to its autoloader.
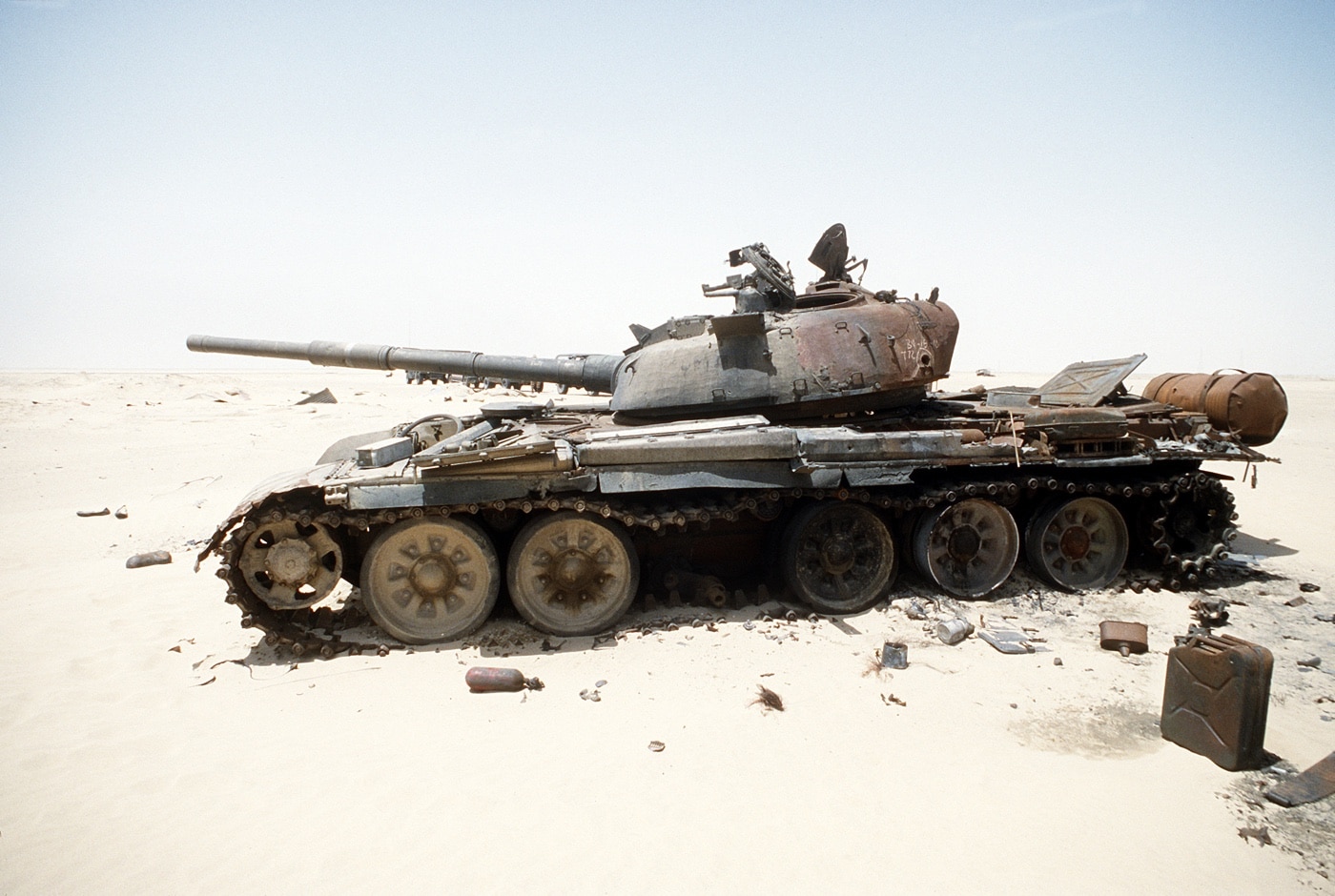

That fatal flaw is why Western tanks, which are larger than the T-72, still rely on a fourth crew to serve as a loader. The shells are retrieved from a sealed and protected compartment and transferred to the gun for firing. It’s a slower process, but it helps ensure that the tank doesn’t become a death trap should it take a hit to the turret.
Surrendering En Masse
The flaw also explains why Russian tank crews have abandoned dozens of T-72s in the nearly a year since the Kremlin launched its unprovoked invasion.
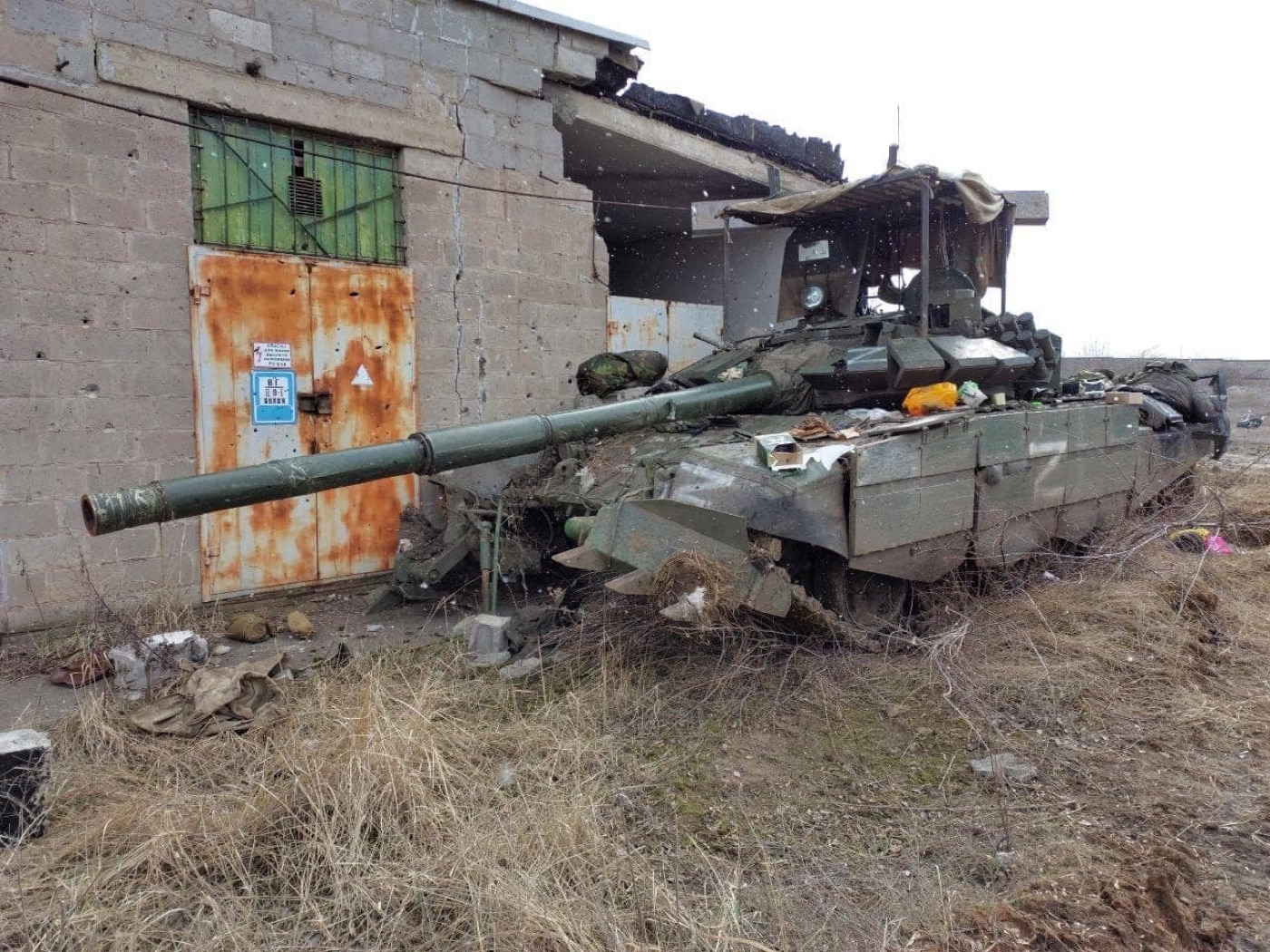

Russia likely expected little resistance, and its troops reportedly arrived with dress uniforms expecting to be greeted as liberators by young women with flowers and ready for a victory parade. Instead, it faced a determined foe, and thanks to Western aid, Kyiv’s forces have steadily pushed back the Russians. Most Western estimates suggest that upwards of 100,000 Russians have been killed — and Ukraine’s Ministry of Defense puts the figure far higher.
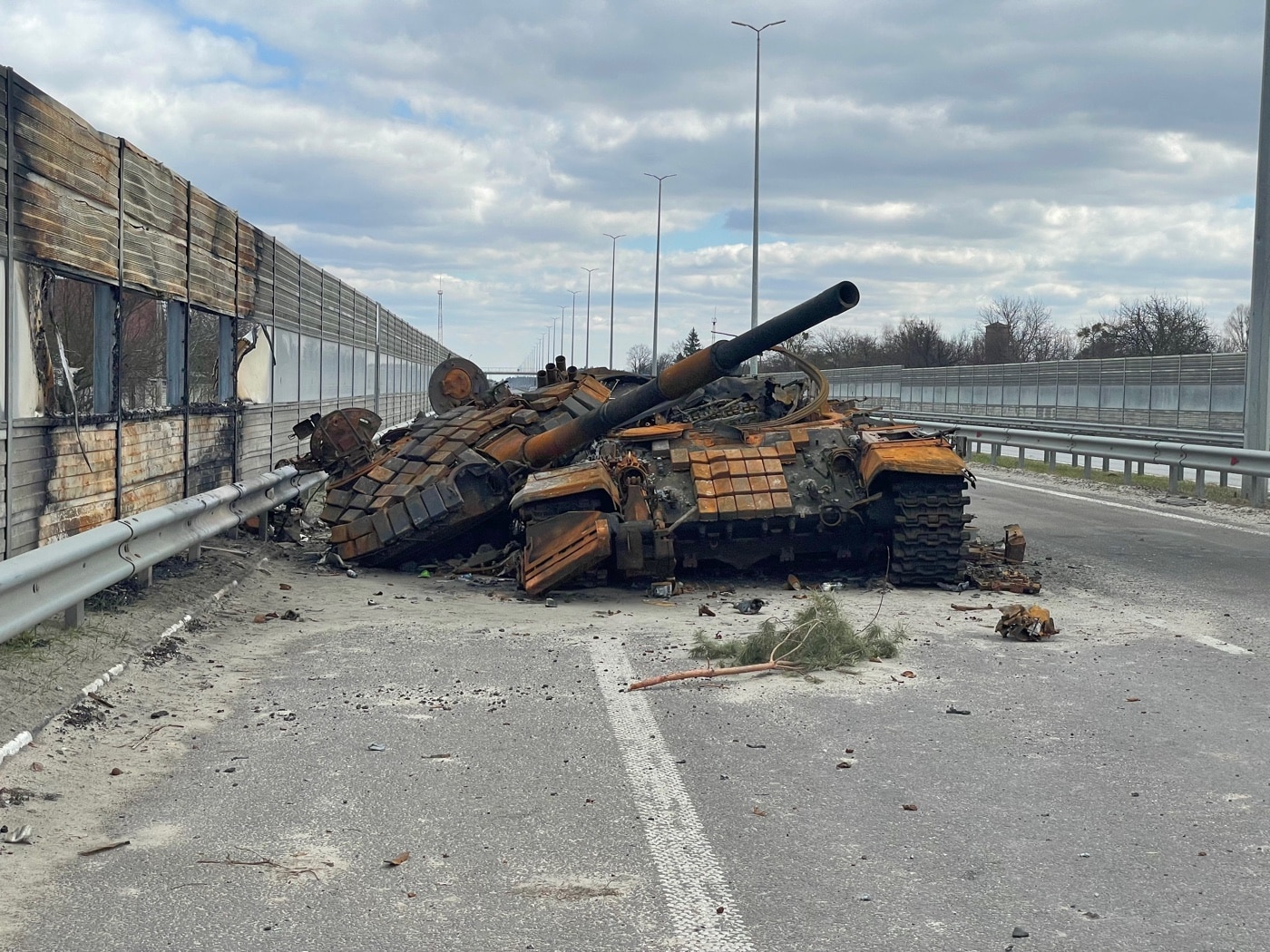

“Russia’s forces didn’t do too well. They lost their ‘best’ front line troops in the early fighting, and the conscripts aren’t sticking around,” said Sanders. “We’re seeing that Igor is home on Tuesday, on the frontlines on Thursday, and dead on Friday. It is especially hard to stay in a tank that has earned a reputation that it is a deathtrap. We’re seeing that the sentiment is ‘I can be in when it takes a hit and goes up in smoke, or I can watch it go while running away.’”
Ukraine Operating the T-72
The interesting footnote is that Ukraine is having far better luck with the T-72. One factor is that its military has better coordination and leadership. Another factor is that its tank crews are simply better. Russia has increasingly relied on those unreliable conscripts, whereas Ukraine has experienced professional tank crews.
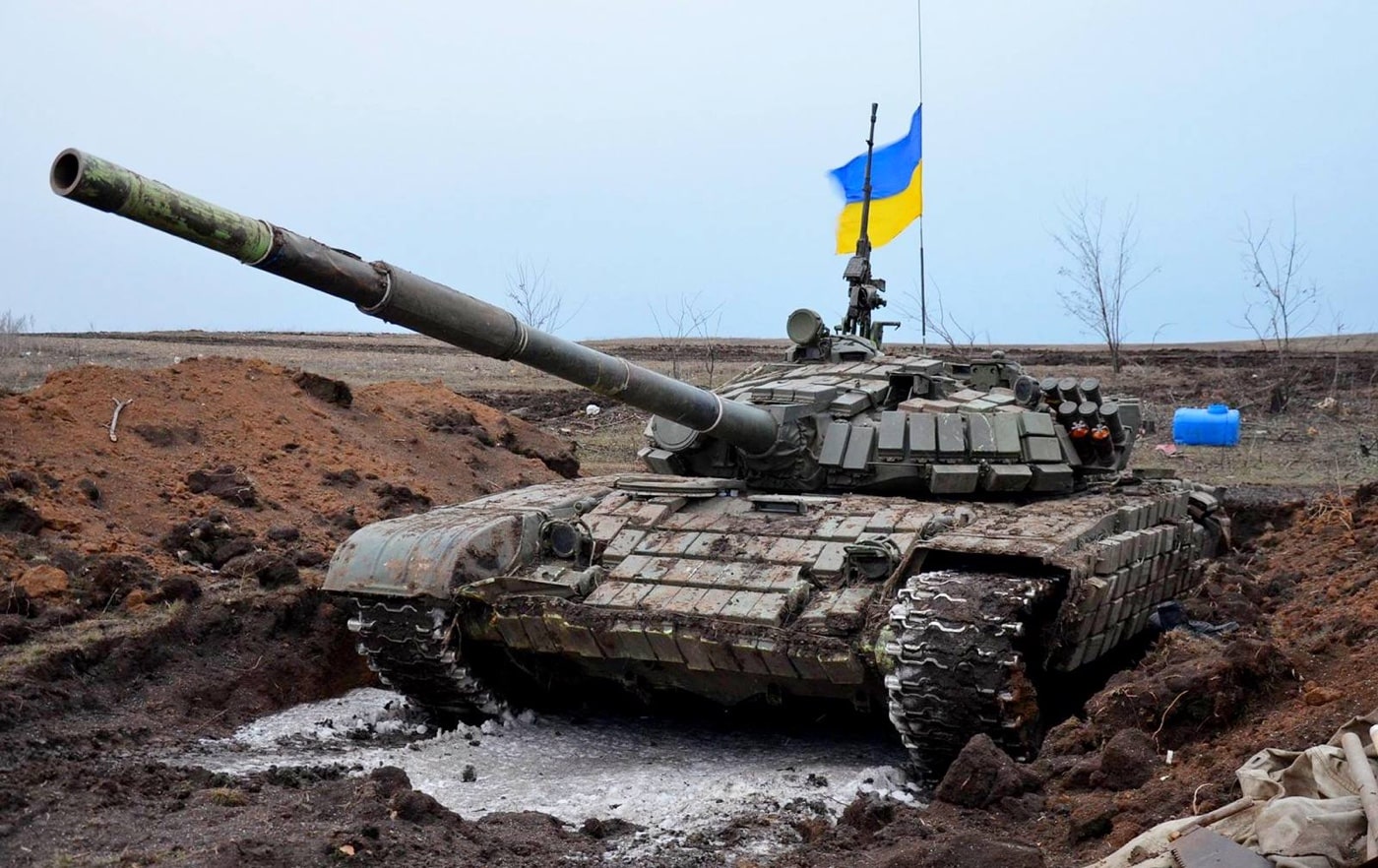

As was noted in the recent Top Gun: Maverick, it isn’t the plane, it is the pilot — and the same holds true of tank crews.
Another factor is that the Ukrainian tanks are increasingly better maintained. Many of its T-72s have come from former Warsaw Pact members including Poland and the Czech Republic. Some of those MBTs have been steadily upgraded by firms such as the Czech-based Excalibur Army. One tank was even signed by Prime Minister of the Czech Republic, Petr Fiala, who offered the brave Ukrainian defenders well wishes in their fight against Russia. By contrast, the Russian tankers likely are told to go out and fight, and probably don’t even hear “good luck.” And it would appear they would need it with the T-72.
Editor’s Note: Please be sure to check out The Armory Life Forum, where you can comment about our daily articles, as well as just talk guns and gear. Click the “Go To Forum Thread” link below to jump in and discuss this article and much more!
Join the Discussion
[ad_2]
Source link
